Start lidar radar
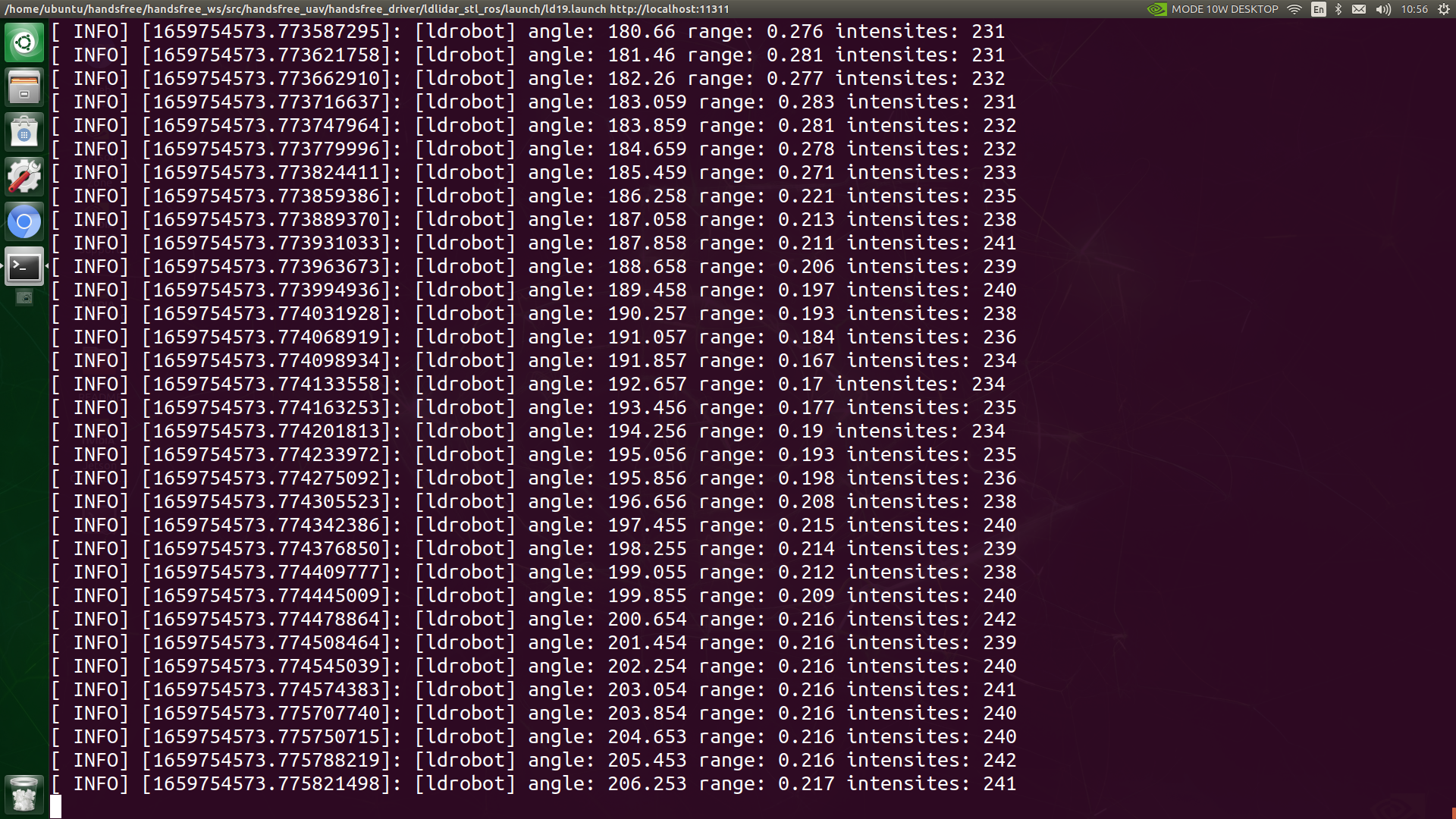
The UAV is equipped with a laser radar. The user can start the radar with the following commands in the new terminal
roslaunch handsfree_lidar lidar.launch
After that, you can see the following output:
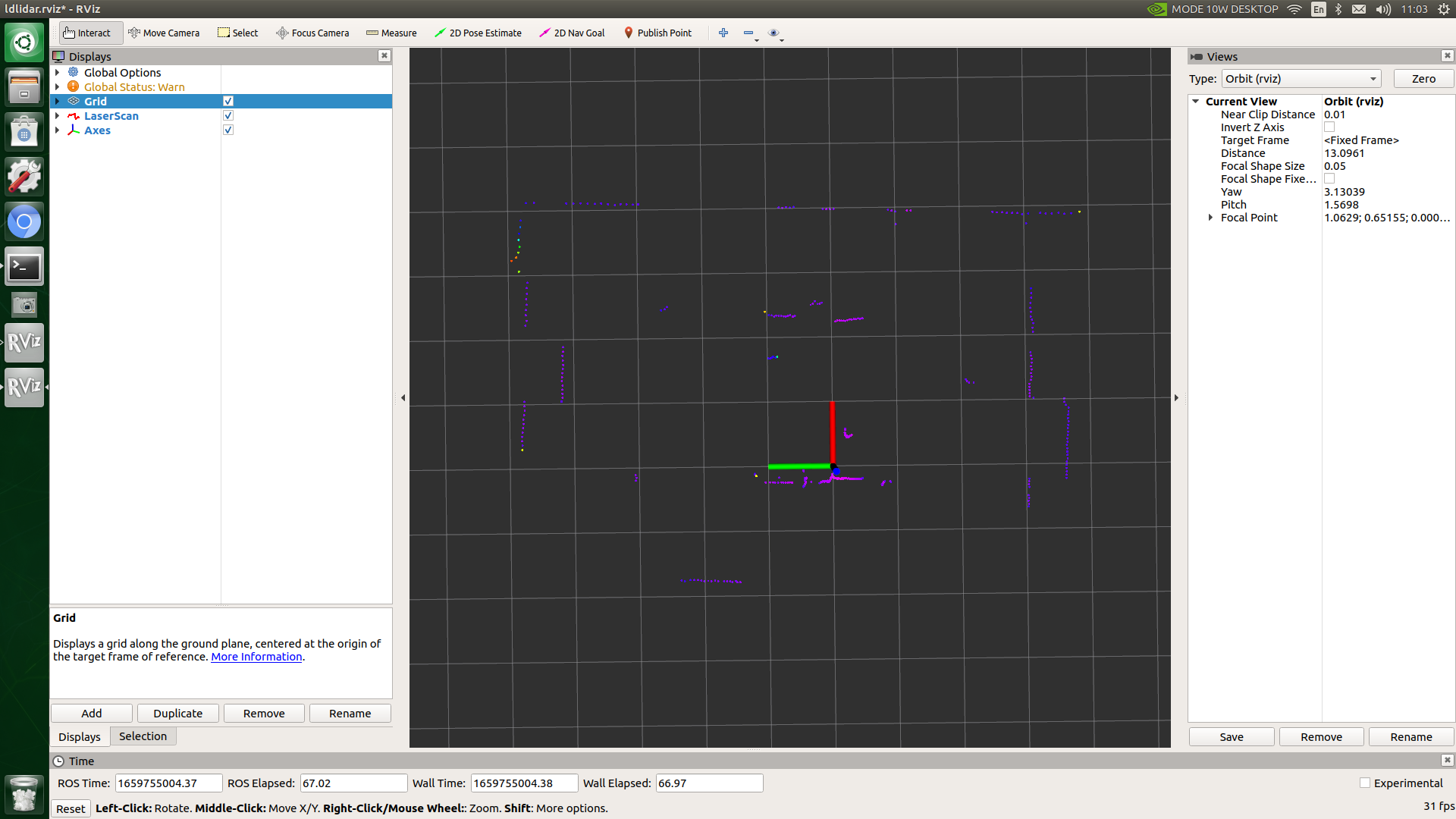
Users can start rviz through the following command to view the radar real-time scanning results:
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find handsfree_lidar`/rviz/view_lidar.rviz
Start depth camera
The user can view the image of realsense camera in two ways:
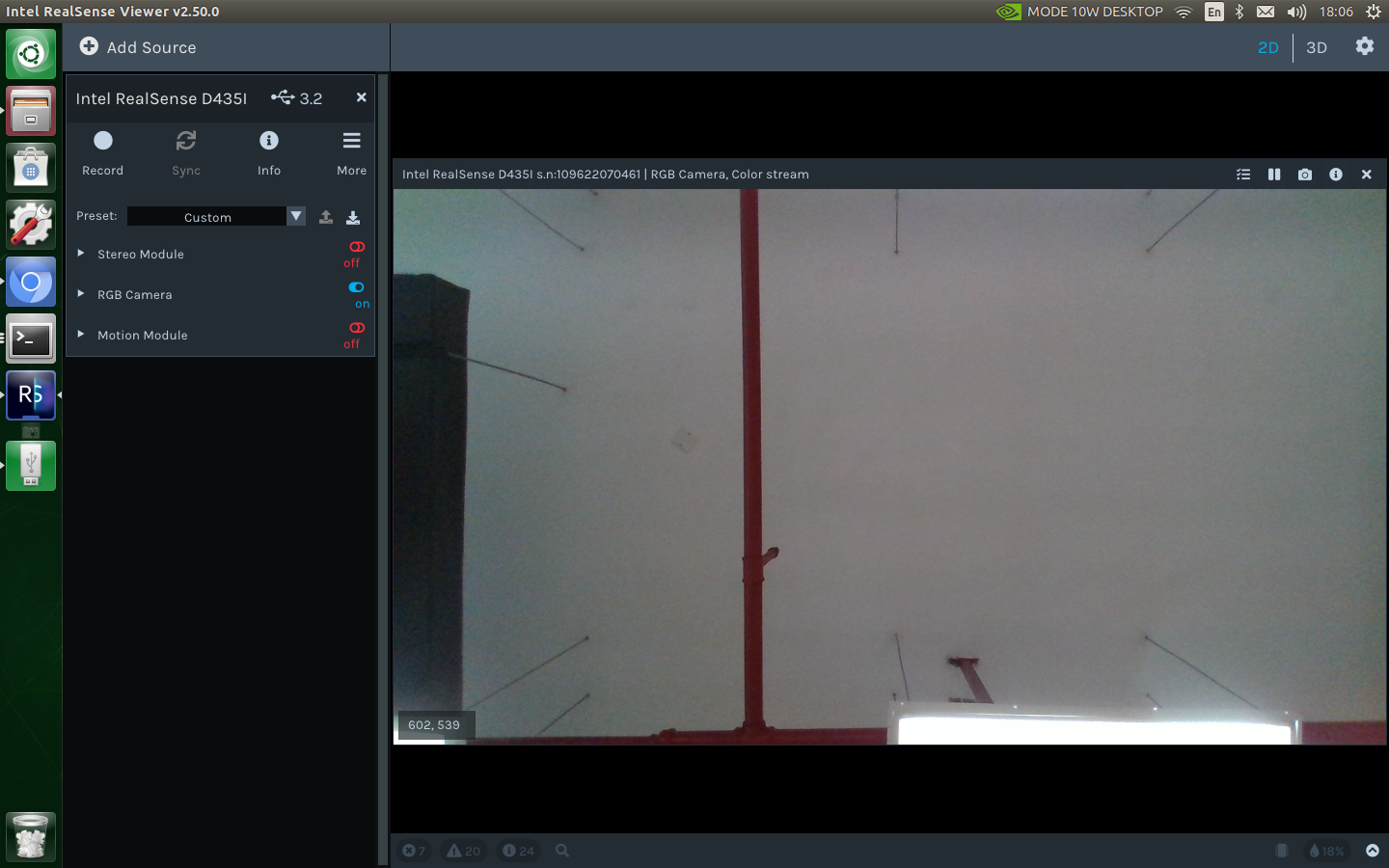
1.Launched through Intel official software
Users can use the following instructions to open the official software of Intel:
realsense-viewer
After that, you can view the RGB image of the realsense depth camera
You can also view the depth image
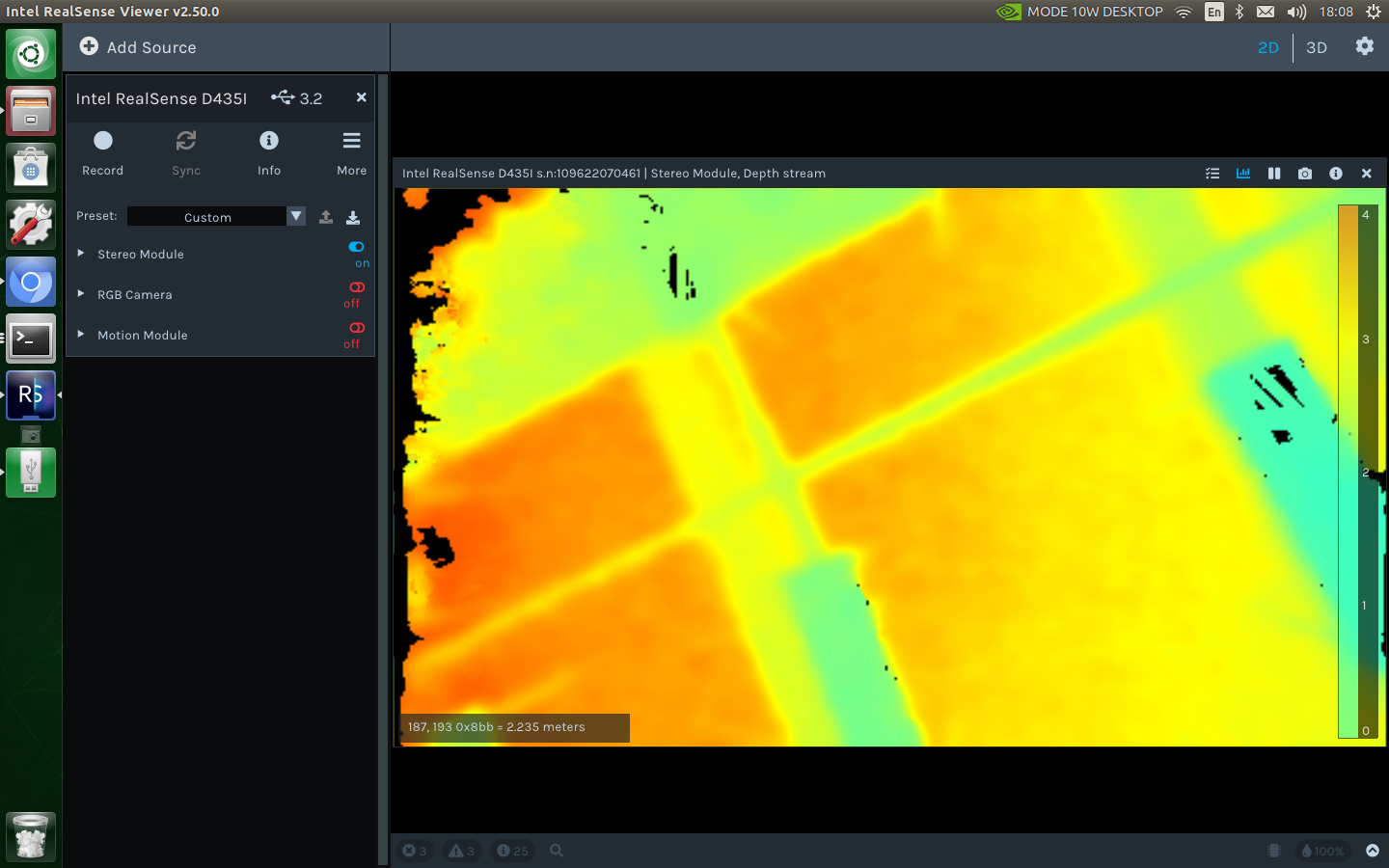
2.Start by ROS drive
The user can start the ROS drive of the realsense depth camera through the following command:
roslaunch handsfree_camera camera.launch
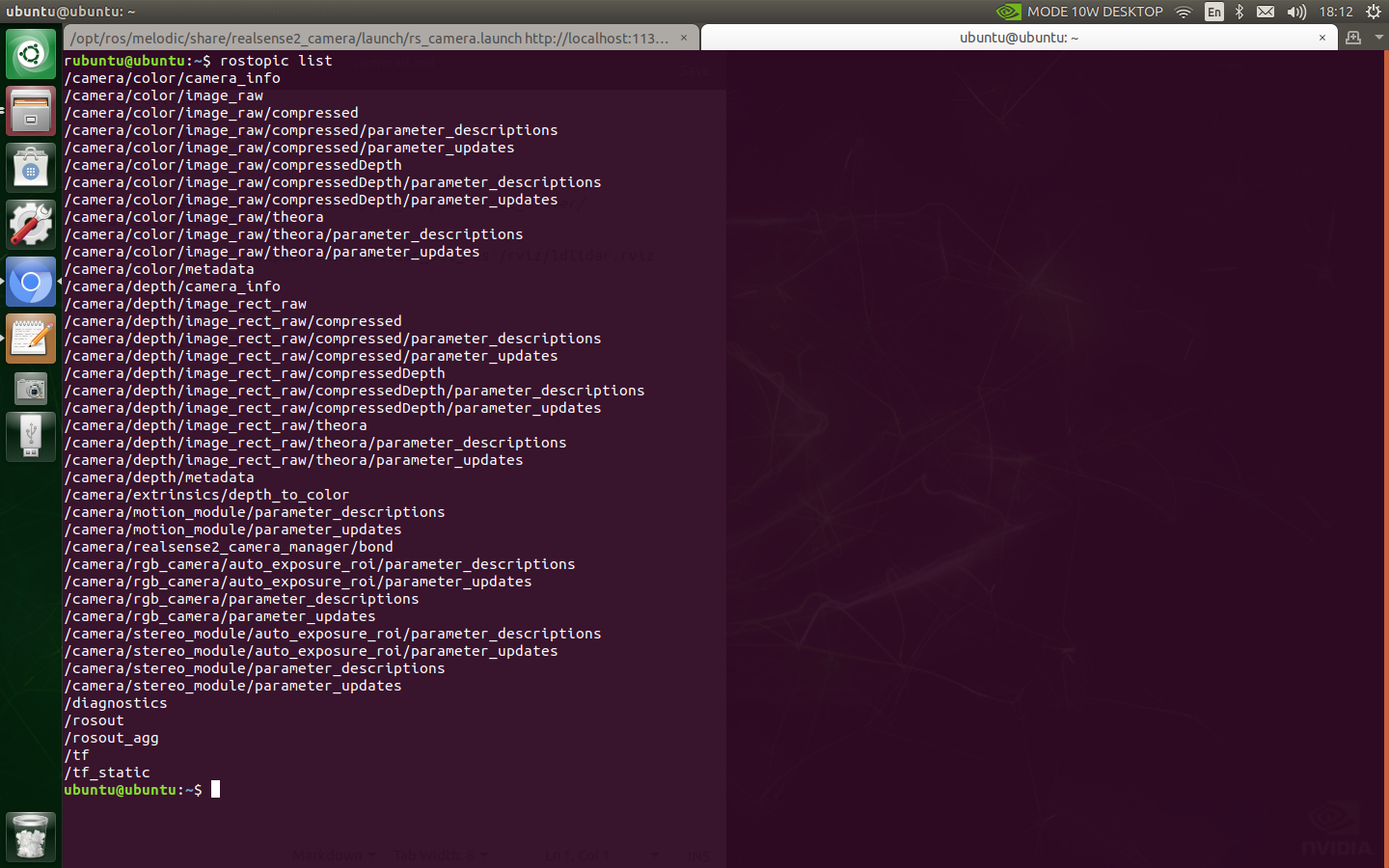
After startup, the following topics can be obtained:
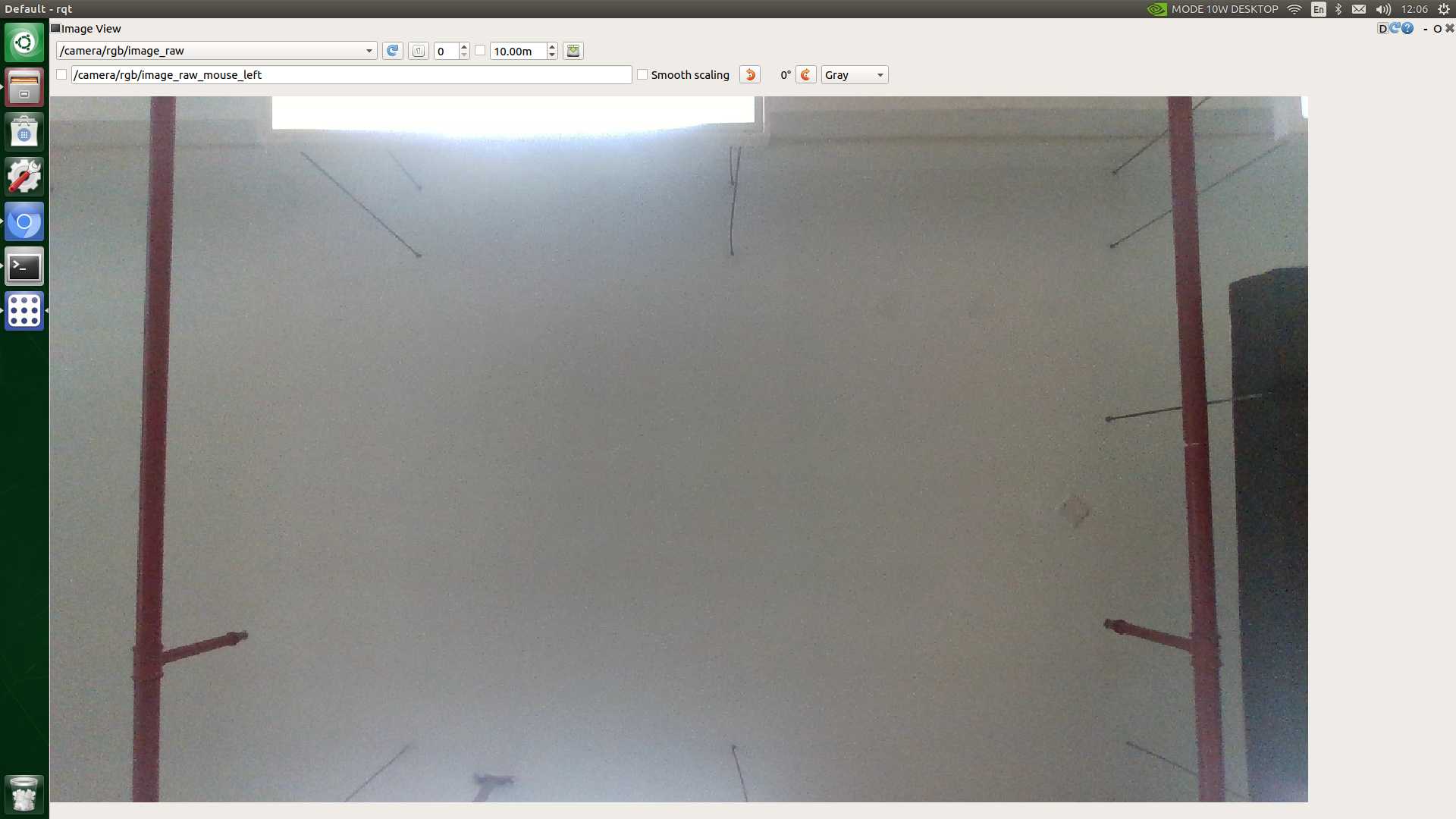
After that, you can view the RGB image of the realsense depth camera through rqt
You can view the depth image of the realsense depth camera
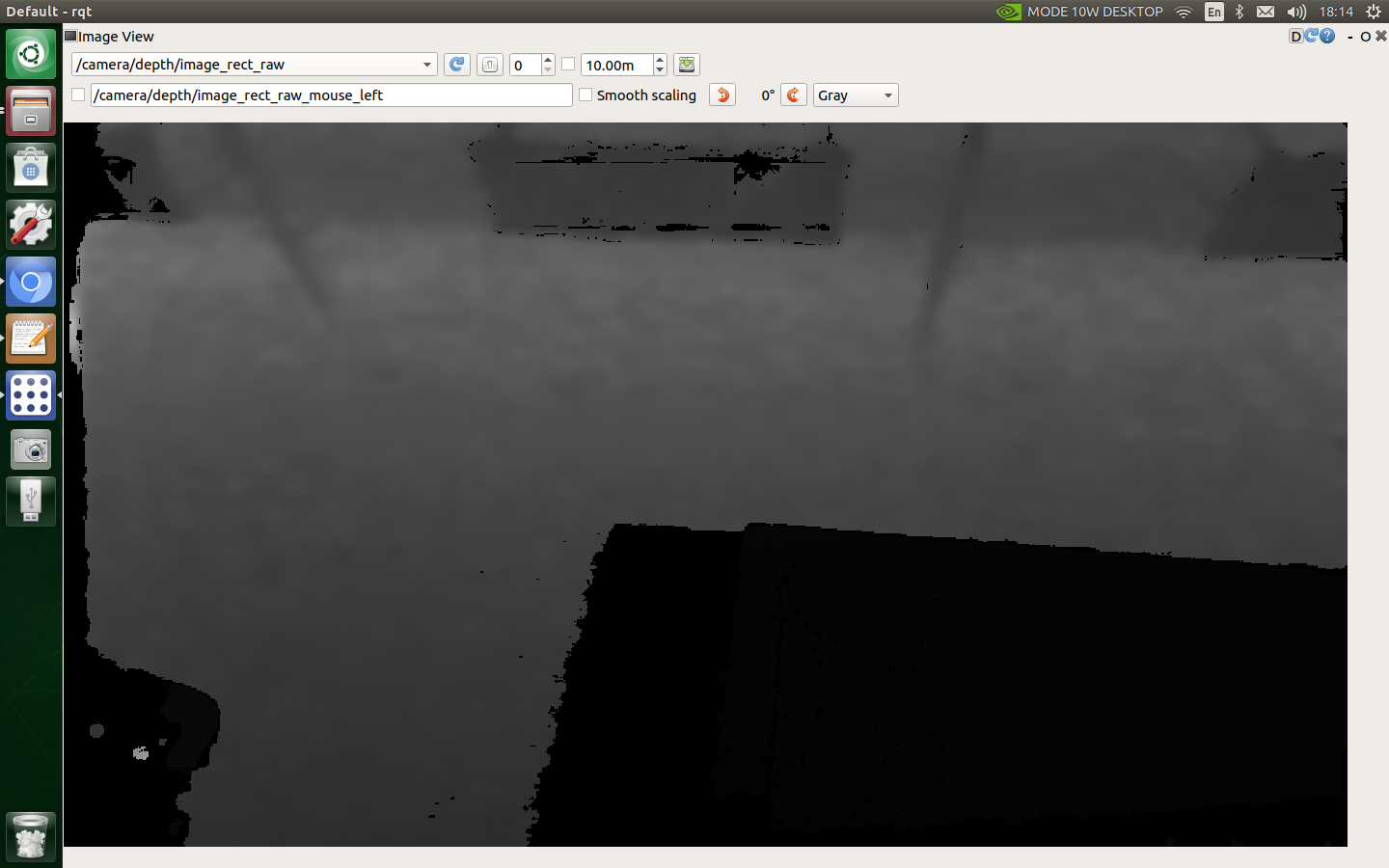
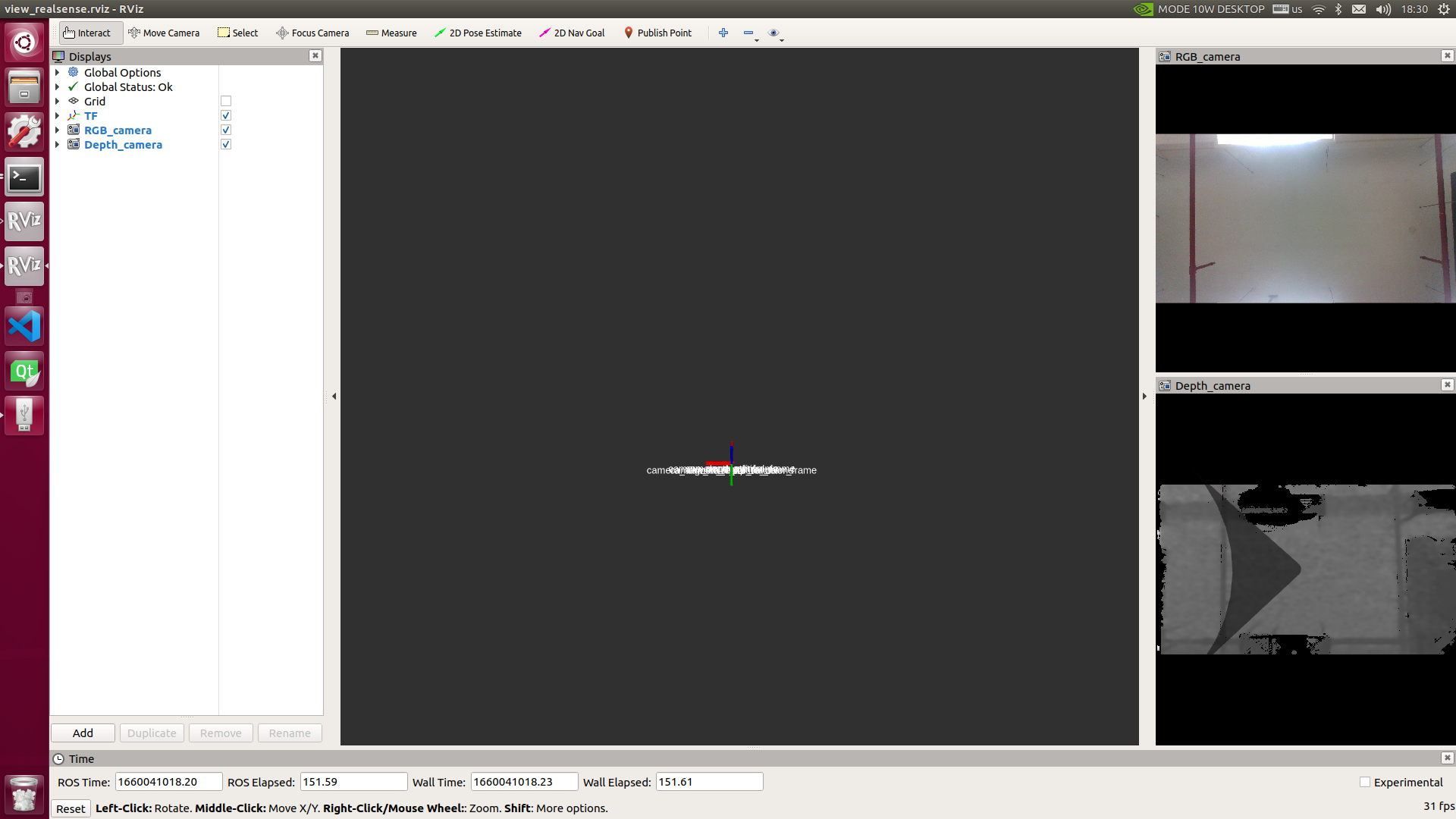
You can also use the following command to view the image of the realsense depth camera through rviz:
rosrun rviz rviz -d `rospack find handsfree_camera`/rviz/view_realsense.rviz
The results are shown in the following figure
Start the underlying driver
This device uses a motion capture and positioning system. Before using it, users need to use the following command in the new terminal to start the underlying driver
roslaunch handsfree_ uav_ hw uav_ hw.launch
The dynamic capture positioning data needs to be forwarded to Mavros for positioning in unmanned mobile capture environments. This launch file includes the start Mavros driver and dynamic capture driver
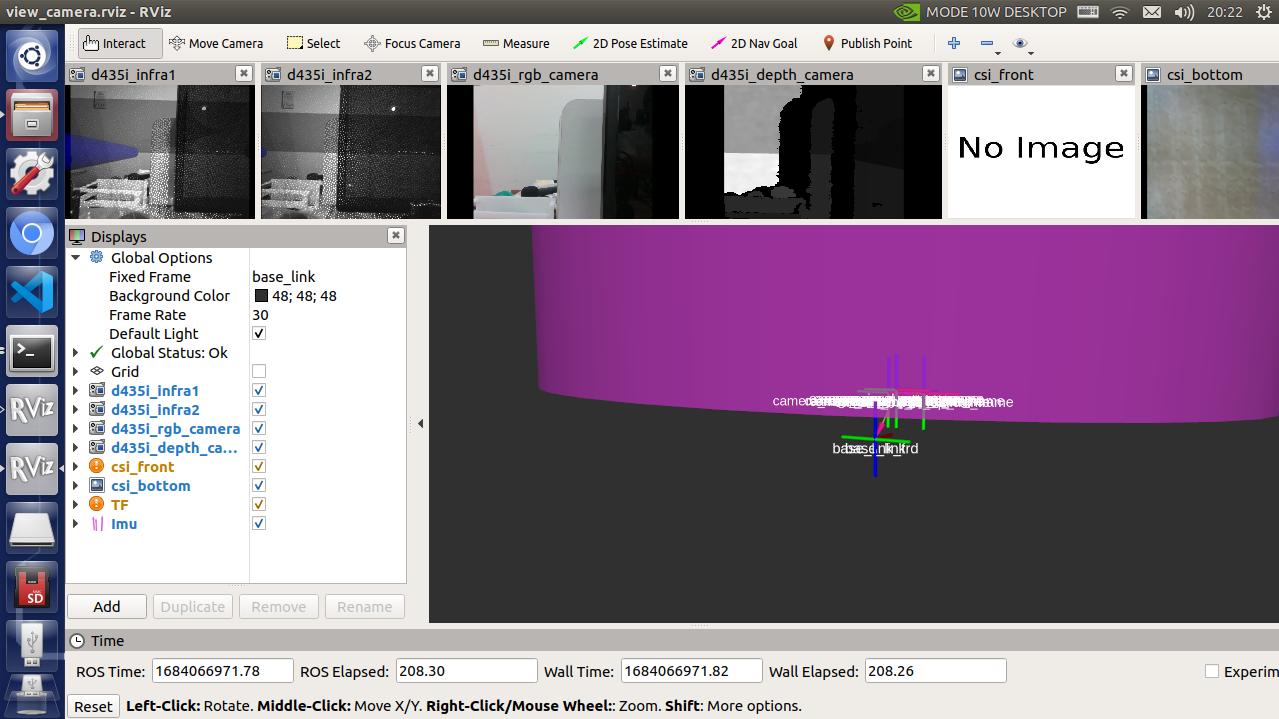
Activate all cameras
This device has two cis cameras and one realsense depth camera. Users can view all of them through the following commands
roslaunch handsfree_ uav_ camera view_ camera. launch
Afterwards, all camera images can be viewed